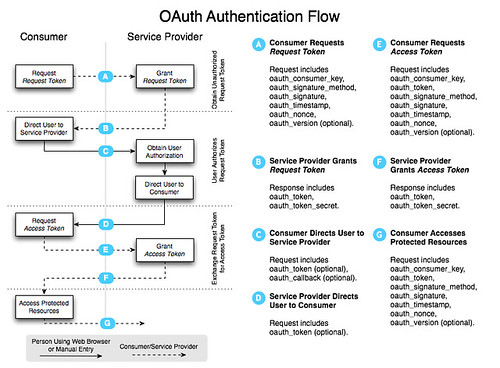
How to do cross-domain GWT RPC with a ProxyServlet
Last week, I started working on a new project using GWT. On my last project, we used GWT HTTP Calls and my new project is using RPC. We'll likely migrate to a JSON backend eventually, but in the meantime, I wanted to be able to develop in hosted mode (localhost:8888) and call services on another host (localhost:8080), where the services are running in a JSF/Spring webapp.
At first, I thought it'd be easy thanks to the handy-dandy ProxyServlet I mentioned in Implementing OAuth with GWT. However, when I tried to hook it in and use it, I saw the following error in my server-side logs.
java.lang.NullPointerException
at javax.servlet.GenericServlet.getServletName(GenericServlet.java:322)
at javax.servlet.GenericServlet.log(GenericServlet.java:277)
at com.google.gwt.user.server.rpc.RemoteServiceServlet.doGetSerializationPolicy(RemoteServiceServlet.java:219)
at com.google.gwt.user.server.rpc.RemoteServiceServlet.getSerializationPolicy(RemoteServiceServlet.java:117)
at com.google.gwt.user.server.rpc.impl.ServerSerializationStreamReader.prepareToRead(ServerSerializationStreamReader.java:429)
at com.google.gwt.user.server.rpc.RPC.decodeRequest(RPC.java:234)
Looking at RemoteServiceServlet.java:219, there's a logging call that fails for some reason (at least in my application).
/*
* Check that the module path must be in the same web app as the servlet
* itself. If you need to implement a scheme different than this, override
* this method.
*/
if (modulePath == null || !modulePath.startsWith(contextPath)) {
String message = "ERROR: The module path requested, "
+ modulePath
+ ", is not in the same web application as this servlet, "
+ contextPath
+ ". Your module may not be properly configured or your client and server code maybe out of date.";
log(message, null);
}
In the above code, you might notice that GWT is checking to make sure the client is hosted in the same application as the server. After I figured this out, it was pretty easy to modify my ProxyServlet to trick GWT RPC into thinking the client was in the same web application. In the ProxyServlet's handleContentPost method, I added the following code to replace "localhost:8888/" with "localhost:8080/services/" (in the content of the post to the server).
if (contentType.startsWith("text/x-gwt-rpc")) {
String clientHost = httpServletRequest.getLocalName();
if (clientHost.equals("127.0.0.1")) {
clientHost = "localhost";
}
int clientPort = httpServletRequest.getLocalPort();
String clientUrl = clientHost + ((clientPort != 80) ? ":" +
clientPort : "");
String serverUrl = stringProxyHost + ((intProxyPort != 80) ? ":" +
intProxyPort : "") + httpServletRequest.getServletPath();
postContent = postContent.replace(clientUrl , serverUrl);
}
After manipulating the posted content, I was successfully able to use GWT RPC cross-domain.
Woo hoo!
For your convenience, the full handleContentPost() method is listed below.
private void handleContentPost(PostMethod postMethodProxyRequest,
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest)
throws IOException, ServletException {
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader reader = httpServletRequest.getReader();
for (;;) {
String line = reader.readLine();
if (line == null) break;
content.append(line);
}
String contentType = httpServletRequest.getContentType();
String postContent = content.toString();
if (contentType.startsWith("text/x-gwt-rpc")) {
String clientHost = httpServletRequest.getLocalName();
if (clientHost.equals("127.0.0.1")) {
clientHost = "localhost";
}
int clientPort = httpServletRequest.getLocalPort();
String clientUrl = clientHost + ((clientPort != 80) ? ":" +
clientPort : "");
String serverUrl = stringProxyHost + ((intProxyPort != 80) ? ":" +
intProxyPort : "") + httpServletRequest.getServletPath();
postContent = postContent.replace(clientUrl , serverUrl);
}
String encoding = httpServletRequest.getCharacterEncoding();
debug("POST Content Type: " + contentType + " Encoding: " + encoding,
"Content: " + postContent);
StringRequestEntity entity;
try {
entity = new StringRequestEntity(postContent, contentType, encoding);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
// Set the proxy request POST data
postMethodProxyRequest.setRequestEntity(entity);
}
Update: In the comments, Ganesh asked for more details, so I figured it'd be a good idea to post the full source code. First of all, click here to see the code for the ProxyServlet:
I generally subclass ProxyServlet to provide my own configuration:
public class MyProxyServlet extends ProxyServlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) {
setFollowRedirects(true);
setRemovePrefix(false);
setProxyPort(8080);
}
}
Here's another example that reads configuration settings from web.xml and proxies to a different domain name:
public class AlternateHostProxyServlet extends ProxyServlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) {
setProxyHost(servletConfig.getInitParameter("proxyHost"));
String secure = servletConfig.getInitParameter("secure");
if (secure != null) {
setSecure(Boolean.valueOf(secure));
}
setFollowRedirects(false);
setRemovePrefix(true);
setProxyPort(80);
}
}
After you've added these to your project, simply map the servlet (and its path) in your *.gwt.xml file (if you're using GWT) and your web.xml.